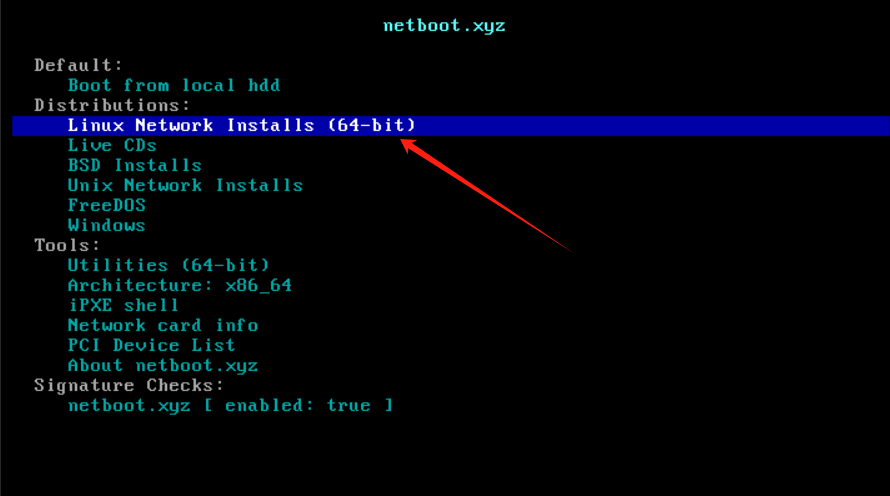
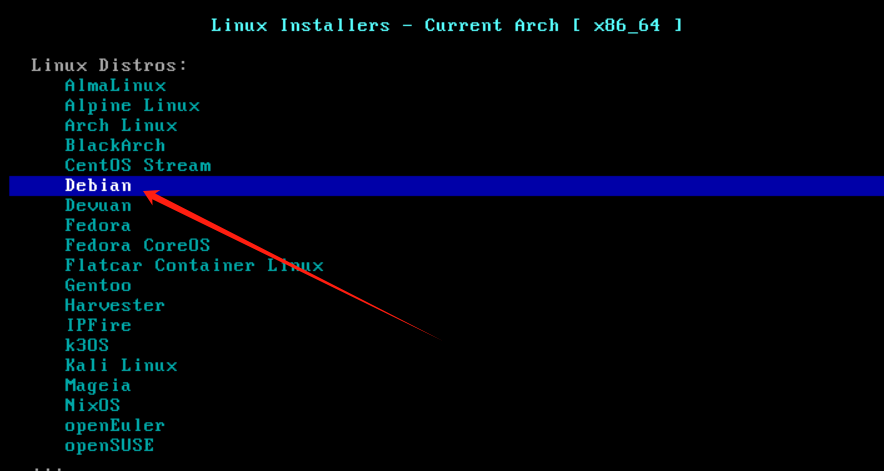
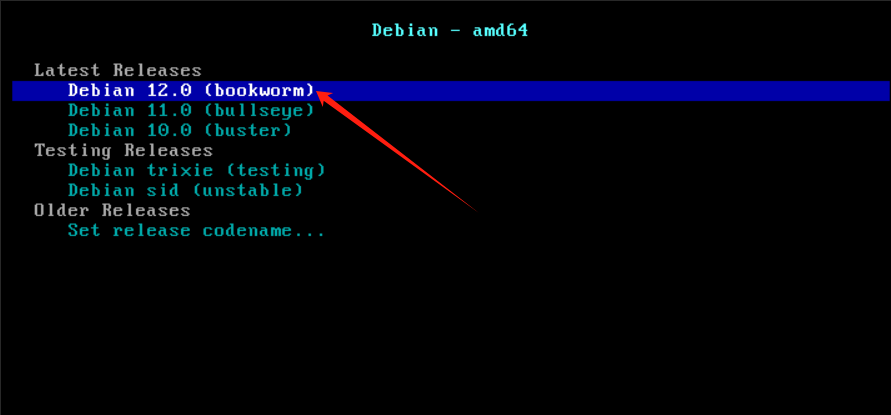
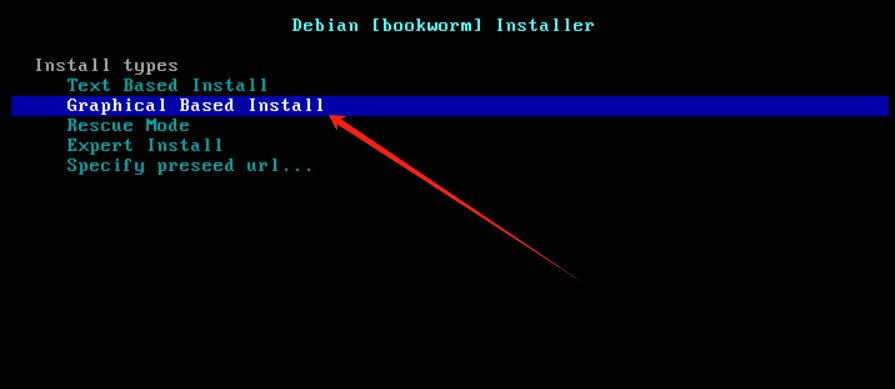
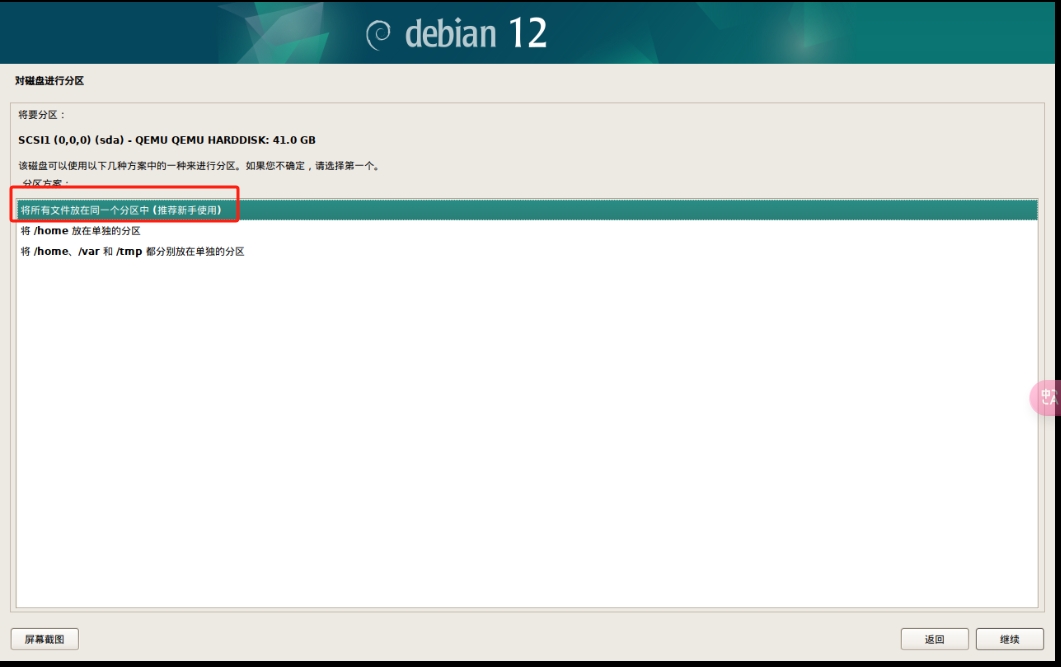
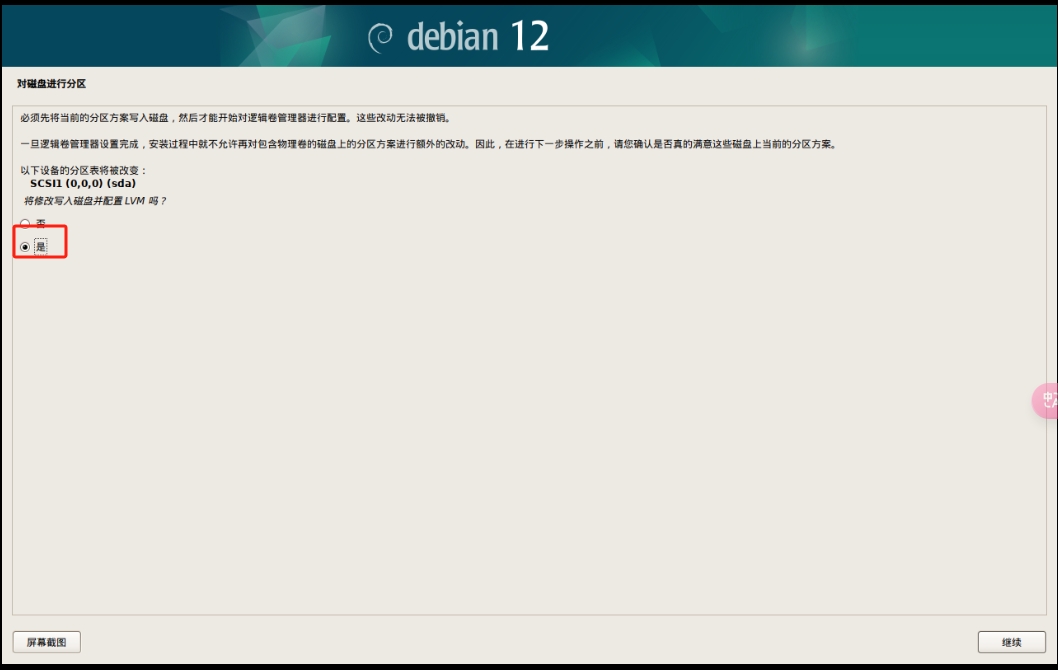
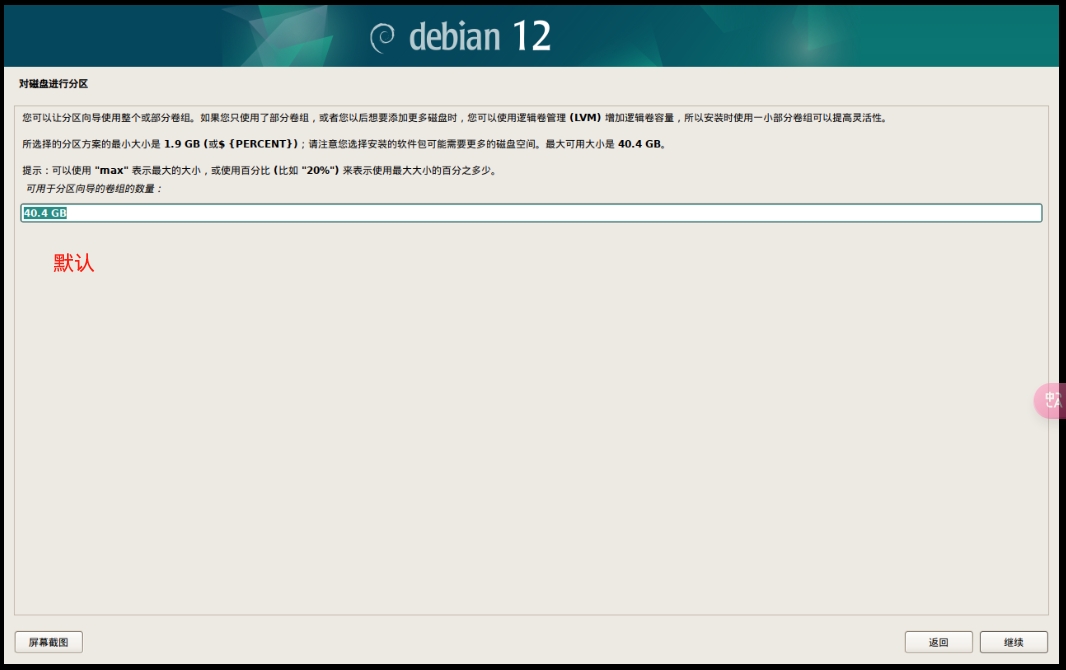
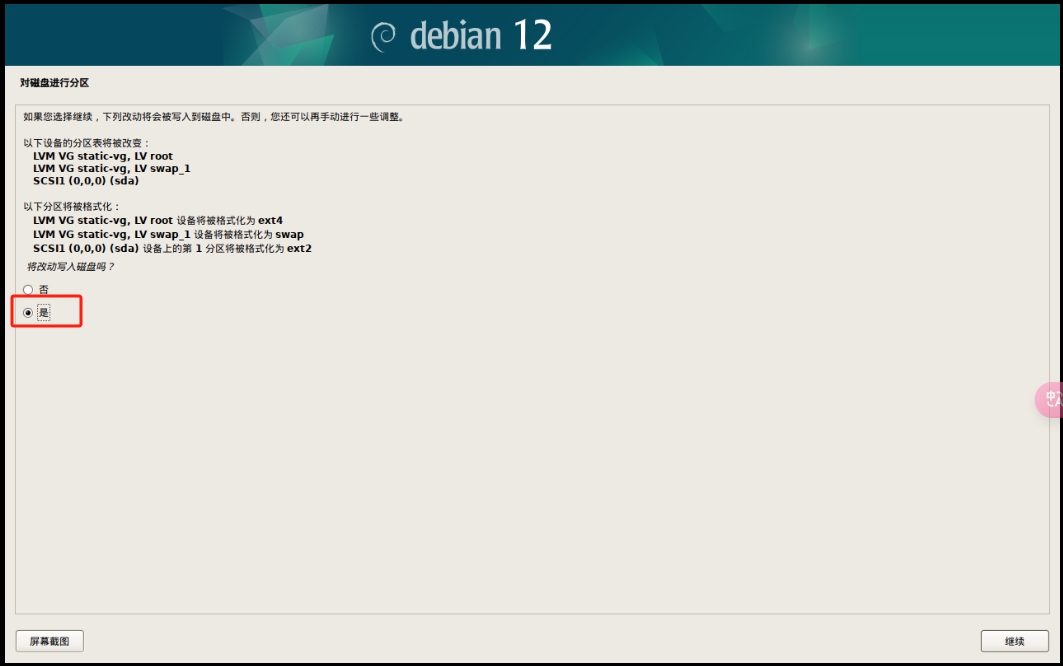
用 BorgBackup/Restic 增量备份Linux文件
以我的环境来作为示例:
我的 NAS 信息:
NAS IP:10.0.2.12
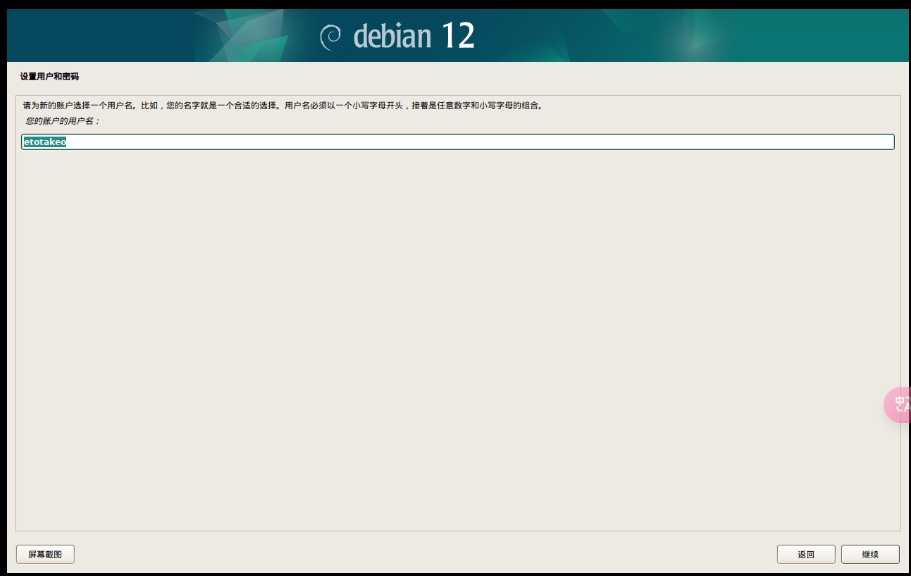
NAS 用户名:etotakeo
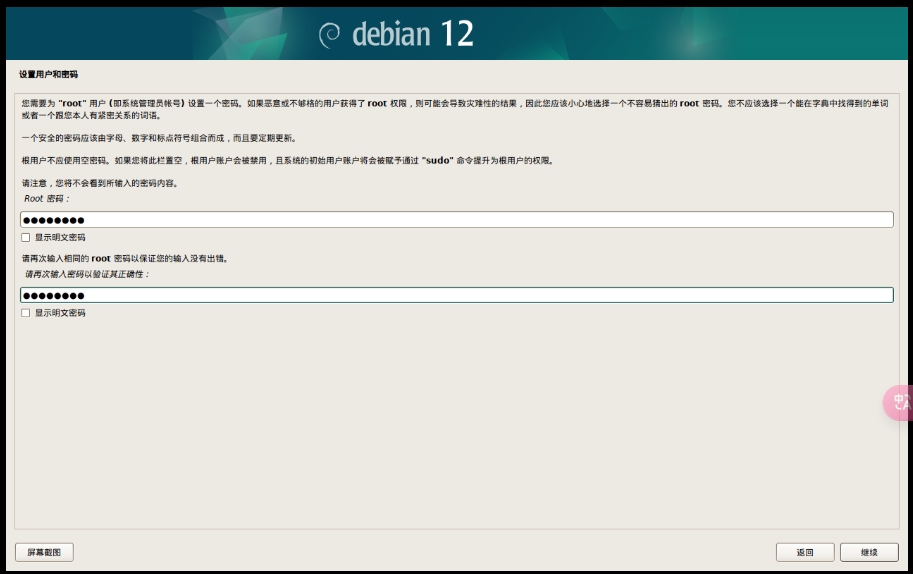
NAS 密码:ng057720
NAS 共享目录:Ext_Flies/Linux备份(自己进去nas确定路径)
`root@DiskStation:/volume2/Ext_Files/Linux整盘备份# pwd
/volume2/Ext_Files/Linux整盘备份`
假设 NAS 用的是 SMB 共享(群晖/威联通常见)
这说明你在 NAS 本机(DiskStation) 上看到的目录。
如果你要从 Linux 主机 上挂载这个目录,通常需要通过 SMB 或 NFS 协议 访问。
比如:
SMB 地址://10.0.2.12/Ext_Files/Linux整盘备份
NFS 地址(如果你在 DSM 里启用了 NFS):10.0.2.12:/volume2/Ext_Files/Linux整盘备份
创建挂载点
sudo mkdir -p /mnt/nas挂载 NAS
把 NAS SMB 路径挂载到 /mnt/nas:
sudo mount -t cifs //10.0.2.12/Ext_Flies/Linux备份 /mnt/nas \
-o username=etotakeo,password=ng057720,vers=3.0,iocharset=utf8iocharset=utf8 保证中文目录不会乱码。
确认挂载成功:
df -h | grep nas初始化 Restic 仓库
先设置密码(写入文件,避免每次输入):
echo "your-restic-password" > /root/.restic-pw
chmod 600 /root/.restic-pw初始化仓库:
export RESTIC_REPOSITORY=/mnt/nas
export RESTIC_PASSWORD_FILE=/root/.restic-pw
restic init注意:为了避免备份一些不必要或会导致问题的目录(例如 /proc、/sys、/dev 等),我们需要排除掉它们。
新建一个排除文件:
nano /root/restic-excludes.txt内容写入(常见排除目录):
/dev/*
/proc/*
/sys/*
/tmp/*
/run/*
/mnt/*
/media/*
/lost+found执行备份:
restic backup / --exclude-file=/root/restic-excludes.txt这样就会把系统整盘数据备份到 NAS 的 /mnt/nas 仓库。
设置定时备份(每天一次)
编辑 cron 任务:
crontab -e添加一行(每天凌晨 2 点执行一次):
0 2 * * * RESTIC_REPOSITORY=/mnt/nas RESTIC_PASSWORD_FILE=/root/.restic-pw /usr/bin/restic backup / --exclude-file=/root/restic-excludes.txt这样每天都会自动备份一次。
每个月备份一次,最多只保留5份
0 3 1 * * RESTIC_REPOSITORY=/mnt/nas RESTIC_PASSWORD_FILE=/root/.restic-pw /usr/bin/restic backup / --exclude-file=/root/restic-excludes.txt && RESTIC_REPOSITORY=/mnt/nas RESTIC_PASSWORD_FILE=/root/.restic-pw /usr/bin/restic forget --keep-last 5 --prune查看已有备份快照
restic snapshots如果这里运行的时候提示:
Fatal: Please specify repository location (-r or --repository-file)
那么试试
restic -r /mnt/nas --password-file /root/.restic-pw snapshots可以看到每次备份的时间和 ID。
恢复数据
你可以按需恢复:
恢复整个系统到某个目录(比如 /restore):
restic restore latest --target /restore这样会把最近的整盘备份恢复到 /restore 目录。
恢复单个文件或目录(例如 /etc/hosts):
restic restore latest --target /restore --include /etc/hosts恢复后你可以从 /restore/etc/hosts 拷贝出来。
NAS 再同步到 OneDrive
你已经说 NAS 会自动备份到 OneDrive,那 restic 在 NAS 上生成的备份文件也会自动被同步上去,等于实现了 本地 + NAS + 云端 三重备份。